The Value of High-Resolution Weather Model
Forecast Data Increased accuracy
Contextual Assessment:
The operator was performing sensitive load/offload operations along coastal areas with highlight on the safety highly engaged when wind is 15knots and above.
Solution:
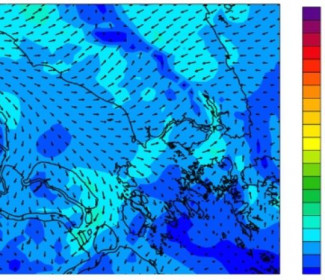
In order to respond to such risk, we implemented Global MeteOcean Numerical Weather (GMONW) solution that could ensure the level of accuracy required by the Operator. Here is the Insight of some results as we designed and implemented specific High-Resolution Weather Model to provide more accurate approach of the meteorological fields in the area of the operating site. WRF (Weather Research and Forecasting), with limit forcing and initialization with the NCEP GFS (Global Forecast System) data flows (with a 0.5-degree / 55km resolution).
GFS
The Global Forecast System (GFS) is a weather forecast model produced by the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP). Dozens of atmospheric and land-soil variables are available through this dataset, from temperatures, winds, and precipitation to soil moisture and atmospheric ozone concentration. The entire globe is covered by the GFS at a base horizontal resolution of 18 miles (28 kilometers) between grid points, which is used by the operational forecasters who predict weather out to 16 days in the future. Horizontal resolution drops to 44 miles (70 kilometers) between grid point for global forecasts between one week and two weeks.
WRF
The Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) Model is a next-generation Mesoscale numerical weather prediction system designed to serve both atmospheric research and operational forecasting needs. It features two dynamical cores, a data assimilation system, and a software architecture facilitating parallel computation and system extensibility. The model serves a wide range of meteorological applications across scales from tens of meters to thousands of kilometers.
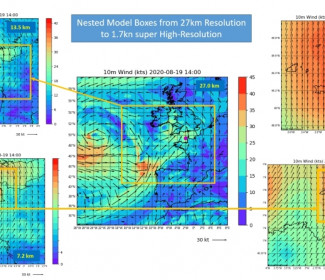
Several nested models with different coverage were implemented as follows:
- First, a large scale (24.3km) grid is used to represent the global trend over the region
- Then, one higher resolution grid (12 km resolution) is used to better forecast the meteorological fields near the operating site.
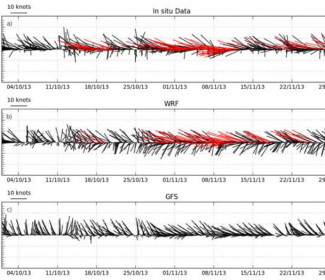
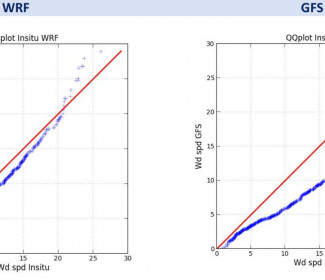
Calibration and the validation of the model was performed by using in-situ meteorological measurements provided by the operator.
Performance:
The performance of the Global MeteOcean High-Resolution model was evaluated by comparing the predictions to the in-situ measurements. A monthly verification performance was done at the end of each month during the service support.
The routine simulation forecast was performed over a period of 5 days with a 6-hourly update.
If you need any advice or specific support, we can help you, do not hesitate to contact us!